Technical SEO in the World of AI
As generative search results continue to reshape the digital landscape, businesses are being pushed to rethink how they approach SEO – especially with the rise of large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT. For those of us who use ChatGPT daily, we know its potential to revolutionise the way people search for and consume information is obvious.
Naturally, a wave of new tools and agencies claim to be at the cutting edge of generative search. But there’s still a lot we don’t know, and even more we can’t yet measure with confidence – as referenced by Jono Anderson.
This uncertainty has sent ripples through the SEO world. The rules might be shifting but the core of good SEO remains the same: making sure your website is technically sound, content-rich, and genuinely useful. In this article, we’ll be exploring what technical SEO checks we do to ensure your website is optimised for generative search.
The Importance of Log File Analysis
Log file analysis is often overlooked in traditional SEO strategies, yet it provides a valuable glimpse into how large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT are accessing your content – providing insight into what data may be used for model training or retrieval, rather than traditional indexing.
Understanding the traffic from these bots can inform your content strategy. Are they engaging with your most important content? Which pages are seeing the most traffic from AI bots? Log files can tell you all of this and more.
After setting a baseline of AI bot traffic, you can start digging into the volume. For example, you might find thousands of requests for certain pages while others receive almost none. By analysing this data alongside your site’s structure and content types, you can spot patterns in AI bot behaviour:
- Are any AI bots blocked? You can test here.
- Are AI bots focusing more on top-level URLs?
- Are product pages being crawled more than blog content?
- Are certain sections of your website being ignored entirely?
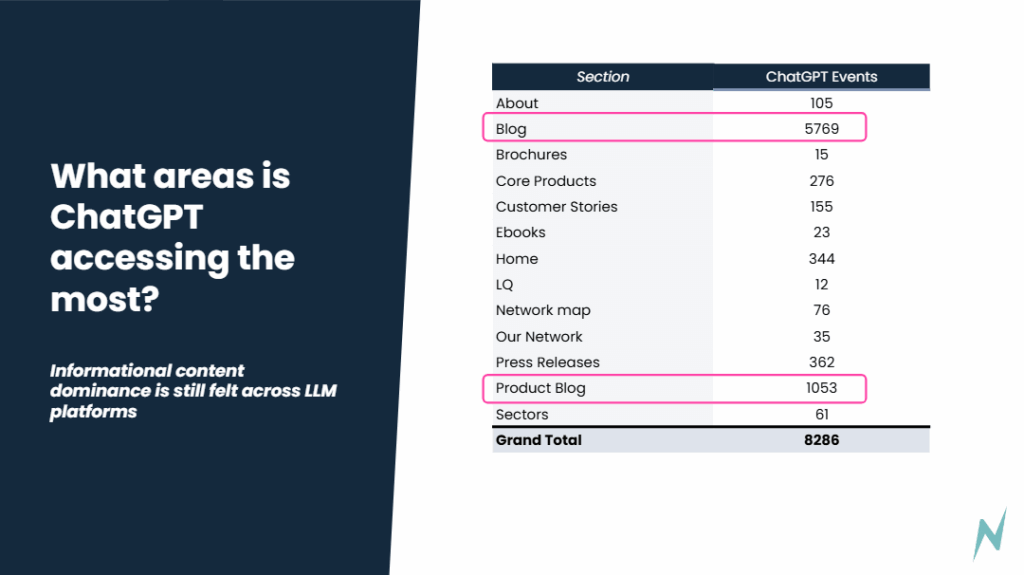
This analysis isn’t one-size-fits-all; it varies by industry. For example, in certain verticals, top-of-funnel content (e.g., blog posts, guides) might get more visibility, while in others, product pages may dominate. Knowing where your website fits into this spectrum helps you prioritise content and identify areas that may need structural adjustments to ensure better AI visibility.
By examining log files, you’ll better understand how AI bots view your site, and you can use this data to refine your SEO approach to cater to this growing traffic source.
The Issue with Javascript and AI Crawlers
AI crawlers face unique challenges when interacting with websites that rely heavily on JavaScript. AI crawlers like GPTBot currently have limited JavaScript rendering capabilities unlike Googlebot, which has built up the processing power to handle it over the years.
Why does this matter for SEO?
It’s simple. If AI bots cannot render JavaScript efficiently, your most important content might not be indexed or prioritised by LLMs.
The Solution: Conduct a JavaScript and Internal Linking Audit
Ensure critical content and internal links are visible in the HTML source, not just rendered client-side. This can be achieved through a JavaScript parity audit. This ensures your website’s JavaScript content doesn’t obstruct important SEO signals.
The Role of Schema in AI
As AI bots continue to evolve, the use of structured data (schema markup) is becoming increasingly important in improving visibility. Early signs are that schema is growing in importance as they aid how AI bots interpret and prioritise content.
Schema allows you to clearly define entities (products, people, organisations, articles) and the relationships between them so that AI systems can understand not just what the page contains, but how it connects to other information.
As such, I think there are a number of schema types that are becoming more important to leverage:
- WebSite Schema by including entities – helps establish a relationship between your content and authoritative resources. For example, you might reference entities within Wikipedia (which holds a 16.3% share of ChatGPT citations) within your schema to help bots better understand your content’s context.
- Article Schema – helps all systems understand that your page is an article, who the author is, when it was published/modified etc.
- Organisation Schema – include key information such as the website address, links to social media profiles and contact details. This all helps Google and LLM platforms to understand more information about the business.
Reporting & Measuring AI Traffic – our new LLM Dashboard
Traditional SEO efforts have long been focused on measurable outcomes: clicks, conversions, and ranking improvements. However, as generative search reshapes discovery, tracking LLM-driven traffic (and revenue for eCommerce brands) is becoming increasingly important. Monitoring visits and conversions from LLM sources by website and landing page helps you see which pages are being surfaced by AI tools, how engaged those users are, and what content or products drive the most value.
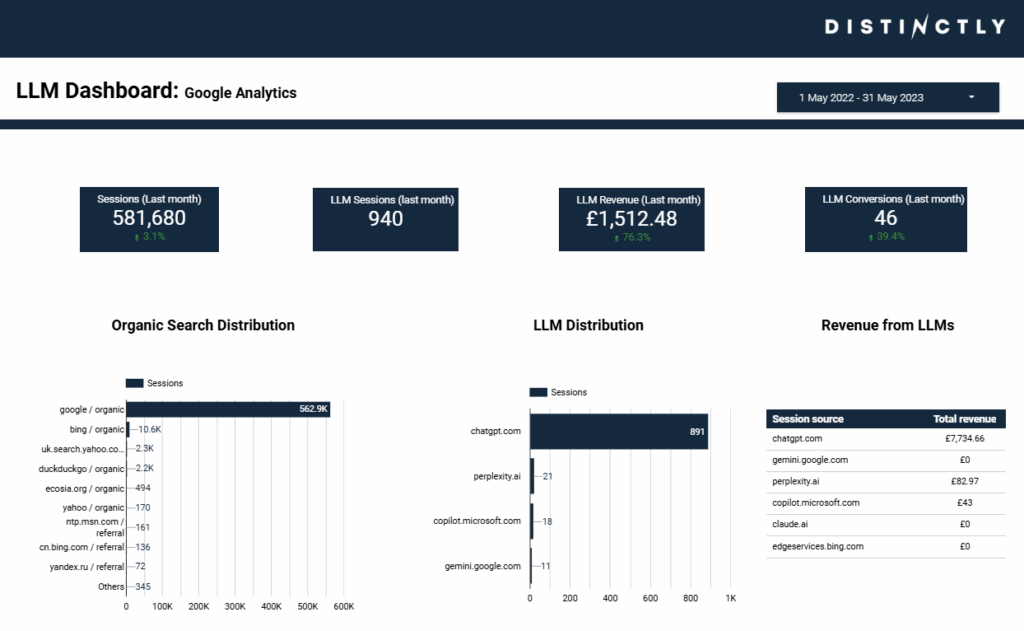
This data reveals whether LLM traffic is high-intent, which product categories or content types perform best, and where to focus future optimisation – such as improving structured data, enhancing product detail, or refining content that AI systems are already drawing from. In short, tracking LLM traffic gives you an early competitive edge in understanding and capitalising on how customers find you through AI-driven experiences.
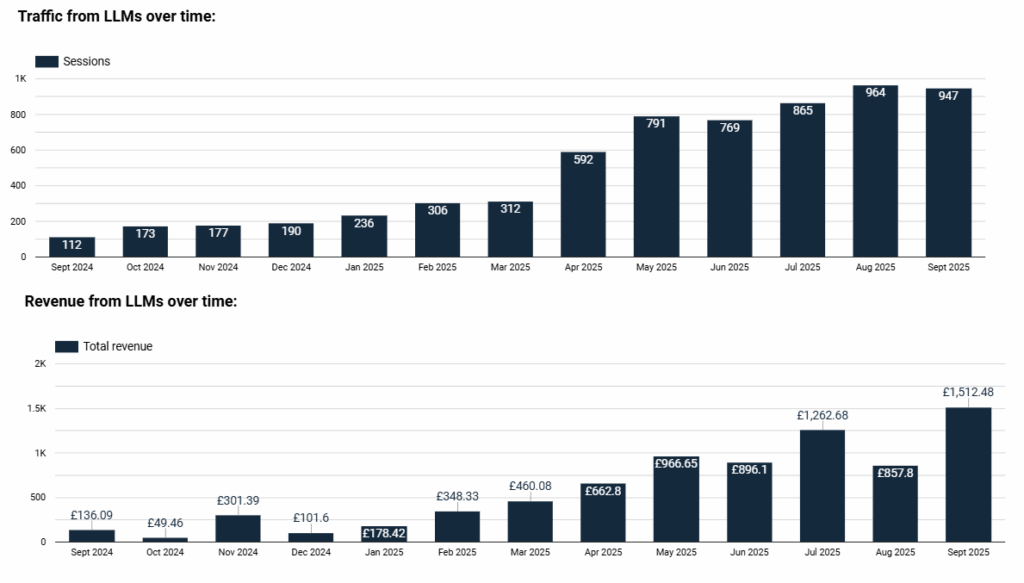
To conclude, the key takeaway for digital marketers is this: investing in comprehensive, accurate and interconnected schema markup isn’t just about getting rich snippets anymore – it’s about ensuring your content is understandable, trusted and usable by LLM’s.